A boiler pressure relief valve (PRV) is a crucial safety device that prevents excessive pressure buildup, ensuring boiler efficiency and safety. Learn its working, benefits, common issues, and maintenance tips.
Boiler systems play a crucial role in various industries, especially in power plants, manufacturing, and heating applications. These systems operate under high pressure, and any abnormal fluctuations can lead to severe consequences, including explosions, equipment failure, and safety hazards for personnel and the environment.
To prevent such risks, every boiler system is equipped with essential safety components, among which the pressure relief valve (PRV) is the most critical. This valve automatically releases excess pressure when it exceeds safe limits, ensuring the system operates efficiently and securely.
Apart from the boiler itself, maintaining all supporting components, including the PRV, is necessary for system reliability. A well-functioning pressure relief valve enhances safety, reduces maintenance costs, and ensures compliance with industry regulations.
In this article, we will explore the working principle, components, benefits, and importance of a boiler pressure relief valve in detail. Understanding its role will help in preventing potential failures and improving overall boiler performance.
What is a Boiler Pressure Relief Valve?
A boiler pressure relief valve (PRV) is a vital safety device used in boiler systems to prevent excessive pressure buildup. It ensures that the boiler operates within safe pressure limits, protecting both the system and surrounding environment from potential hazards such as explosions or equipment failure.
When the pressure inside a boiler exceeds the preset limit, the PRV automatically opens, allowing excess steam, water, or gas to escape. This helps stabilize the pressure and prevents damage to the boiler. Once the pressure returns to a safe level, the valve closes automatically to maintain normal operation.
PRVs are commonly used in power plants, industrial boilers, and heating systems to enhance safety and efficiency. Factors such as clogged pipelines, overheating, or malfunctioning components can cause pressure surges, making the PRV an essential component for preventing dangerous conditions.
Regular maintenance and testing of the pressure relief valve are necessary to ensure its reliability. A faulty PRV may either fail to release pressure when needed or remain open, causing system inefficiency. Proper installation, usually near the boiler, enhances its effectiveness in safeguarding the system.
Overall, a boiler pressure relief valve plays a critical role in pressure management, system longevity, and workplace safety.
Internal Parts of Relief Valve
The pressure relief valve consists of four main parts:
- Spindle – Transfers force from pressure buildup.
- Valve Cap – Protects internal components.
- Spring – Controls valve opening and closing.
- Valve Seal – Prevents leaks and maintains system integrity.
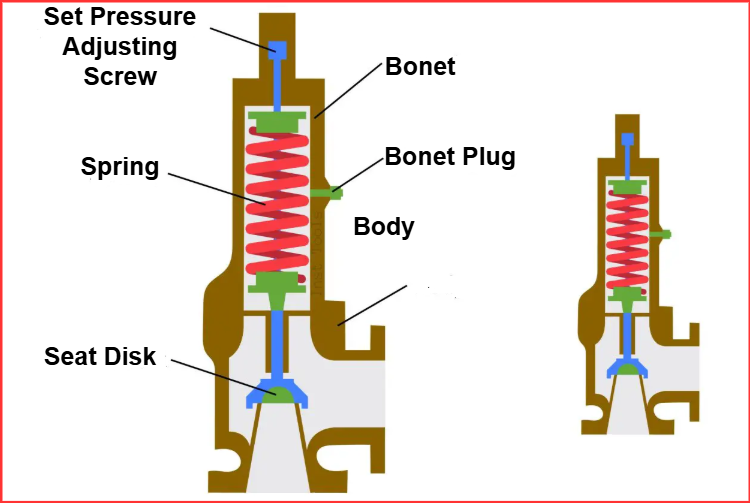
How does a pressure relief valve work?
A boiler pressure relief valve (PRV) is a critical safety component designed to maintain safe pressure levels within a boiler system. It operates automatically to release excess pressure, preventing system failure or damage. Below is the detailed working mechanism of the PRV:
1. Normal Operation
Under normal conditions, the valve remains closed to keep the inlet and outlet disconnected. The system operates at its designated pressure, and no excess steam, water, or gas is released. The spring inside the valve holds the seal tightly in place, ensuring that no leakage occurs.
2. Pressure Increase
When the pressure inside the boiler starts to rise beyond the safe limit, the excess force pushes against the valve seal. This pressure is transmitted to the spindle, which in turn compresses the spring inside the valve. The force applied to the spring depends on the level of pressure increase.
3. Relief Action
Once the pressure crosses the set threshold, the compressed spring forces the valve open. This allows excess steam, water, or gas to escape through the outlet, relieving the pressure inside the boiler. The more the pressure increases, the wider the valve opens, allowing more media to pass through.
4. Pressure Stabilization
As excess pressure is released, the system begins to return to normal operating conditions. With decreasing pressure, the spring inside the valve starts to expand back to its original position, pushing the spindle and valve seal back into place. Once the pressure normalizes, the valve automatically closes, ensuring efficient operation without further loss of steam, water, or gas.
This self-regulating mechanism ensures that the boiler system remains safe, efficient, and free from potential hazards related to overpressure.
Common PRV Issues & Maintenance
A boiler pressure relief valve (PRV) is a critical safety component, but like any mechanical device, it can develop issues over time. One common problem is a stuck-open valve, which continuously releases pressure even when it’s not needed, leading to water or steam wastage and reduced boiler efficiency. Another issue is a failure to activate, where the valve does not release excess pressure when required, posing a serious safety risk. This can be caused by corrosion, debris buildup, or a weakened spring mechanism.
To ensure PRVs function properly, regular inspections and maintenance are essential. Routine checks help identify wear and tear, leaks, or blockages that could compromise valve performance. Cleaning the valve and testing its activation pressure at scheduled intervals can prevent malfunctions. In industrial settings, professional calibration and testing should be conducted as per manufacturer guidelines.
Proper installation is also key to PRV efficiency. The valve should be positioned near the boiler to provide immediate pressure relief when required. Additionally, operators should monitor pressure fluctuations and replace faulty valves promptly to maintain system safety and efficiency.
By following a proactive maintenance approach, industries can enhance boiler performance, ensure regulatory compliance, and prevent costly downtime.
Benefits of a Boiler Pressure Relief Valve
✔ Prevents Boiler Damage – The valve regulates pressure, preventing excessive buildup that could lead to equipment failure or explosions.
✔ Reduces Maintenance Costs – By maintaining safe pressure levels, it minimizes wear and tear, extending the boiler’s lifespan and reducing repair expenses.
✔ Ensures Regulatory Compliance – PRVs help industries comply with safety standards, avoiding legal penalties and operational shutdowns.
✔ Enhances Workplace Safety – By preventing sudden pressure surges, it protects workers and surrounding equipment from hazardous incidents.
✔ Improves System Efficiency – A properly functioning valve ensures consistent pressure levels, optimizing boiler performance and fuel efficiency.
✔ Prevents Operational Downtime – Avoiding pressure-related failures reduces the risk of unexpected shutdowns, ensuring smooth and uninterrupted operations.
Conclusion
A boiler pressure relief valve (PRV) is a crucial safety component that ensures the safe and efficient operation of boiler systems. It prevents excessive pressure buildup, reducing the risk of system failure, explosions, and costly repairs. Proper installation, regular maintenance, and timely replacements are essential to keep PRVs functioning effectively.
By maintaining safe pressure levels, PRVs not only enhance boiler longevity but also help industries comply with safety regulations. Neglecting PRV maintenance can lead to severe consequences, including equipment damage and operational downtime. Therefore, routine inspections and testing should be prioritized to ensure reliability.
In summary, a well-maintained pressure relief valve is a key factor in industrial boiler safety, efficiency, and overall performance.
Read Next: