Discover the fundamental laws of thermocouple—Homogeneous Materials, Intermediate Metals, and Intermediate Temperatures. Learn how these principles govern accurate temperature measurement in scientific and industrial applications.”
Thermocouples are essential devices used for temperature measurement in various scientific and industrial applications. These devices operate based on the thermoelectric effect, which involves the generation of an electrical voltage when there is a temperature difference between two different metals or alloys. The functioning of thermocouples is governed by three fundamental laws: the Law of Homogeneous Materials, the Law of Intermediate Metals, and the Law of Intermediate Temperatures. Understanding these laws of thermocouples is crucial for their proper application and accurate temperature measurement.
The following empirically derived laws of thermocouple are useful for understanding, diagnosing, and utilizing thermocouples.
1. Law of Homogeneous Materials
The Law of Homogeneous Materials states that a thermoelectric current cannot be generated in a circuit made of a single homogeneous material, regardless of the temperature distribution along its length, as long as the material is homogeneous and no external electromotive forces are applied. This law highlights the importance of using two materials to form a thermocouple junction. It can be summarized as:
- Homogeneous Material: No thermoelectric voltage is produced if the circuit is made of a single, continuous material.
- Different Materials Required: For a thermocouple to produce a voltage, it must consist of two dissimilar conductors.
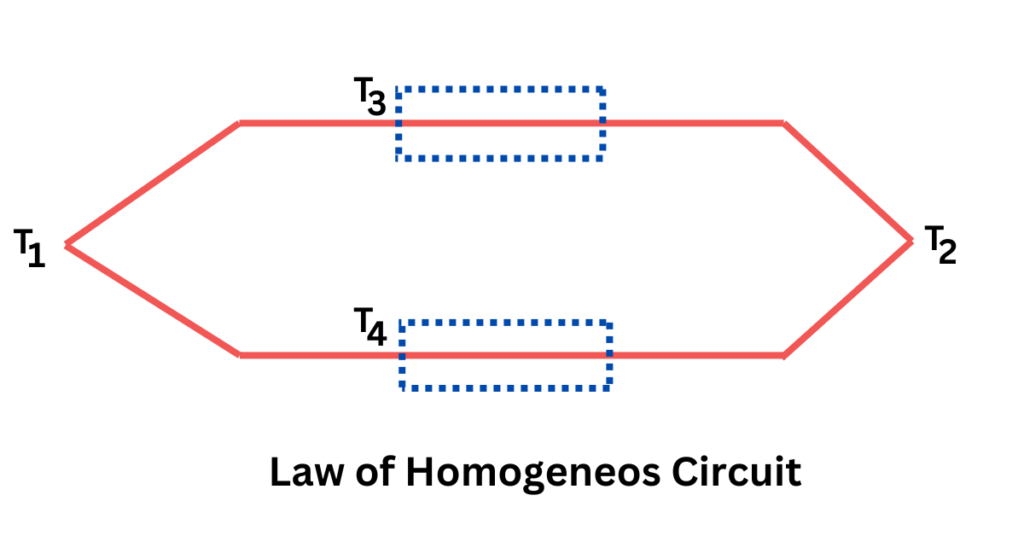
The figure above depicts a thermocouple with junction temperatures T1 and T2. The temperatures along the thermocouple wires are T3 and T4. Despite this, the thermocouple emf depends solely on the temperature gradient T2 – T1.
2. Law of Intermediate Metals
The Law of Intermediate Metals states that introducing an intermediate metal into a thermocouple circuit will not affect the generated thermoelectric voltage, provided the junctions between the intermediate metal and the original materials are at the same temperature.
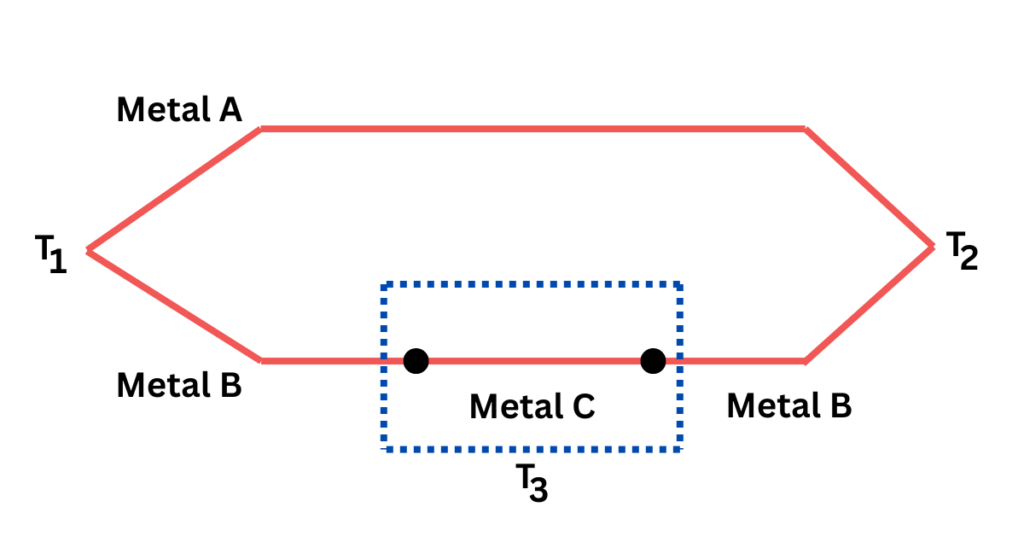
This law is fundamental for the practical use of thermocouples, as it allows for the extension of thermocouple wires and the connection of measurement instruments without altering the temperature reading. The key points of this law are:
- Intermediate Metal Introduction: Inserting another metal into the circuit does not change the thermocouple’s output voltage.
- Temperature Equality: The junctions the intermediate metal creates must be at identical temperatures.
3. Law of Intermediate Temperatures
The Law of Intermediate Temperatures states that if a thermocouple produces a voltage V1 when its junctions are at temperatures T1 and T2, and a voltage V2 when its junctions are at temperatures T2 and T3, then it will produce a voltage V equal to V1+V2 when the junctions are at temperatures T1and T3.
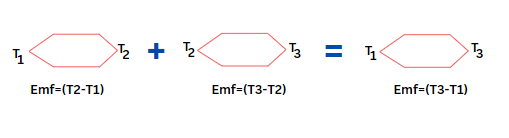
This law allows for calculating thermoelectric voltage across a range of temperatures using known values. The law can be broken down as follows:
- Additive Property: The voltage generated across multiple temperature ranges is the sum of the voltages for each range.
- Temperature Relationship: This additive property helps derive the voltage from smaller, known temperature ranges for a wide temperature span.
Practical Implications of the Laws of Thermocouples
Understanding and applying the laws of thermocouples is critical for accurate temperature measurement in practical scenarios. Here are some practical implications:
- Material Selection: The Law of Homogeneous Materials governs the choice of appropriate materials for thermocouples, which is essential to ensuring accurate readings.
- Circuit Design: When designing circuits with thermocouples, the Law of Intermediate Metals ensures that connecting wires and measurement devices do not affect the temperature readings.
- Calibration and Measurement: The Law of Intermediate Temperatures aids in calibrating thermocouples and predicting their behavior across different temperature ranges.
Conclusion
The laws of thermocouples provide a theoretical foundation for understanding how these devices work and ensuring accurate temperature measurement in various applications. By following the Laws of Homogeneous Materials, Intermediate Metals, and Intermediate Temperatures, engineers and scientists can design reliable thermocouple systems and extend their functionality while maintaining precision. These fundamental principles are crucial for effectively and efficiently using thermocouples in temperature measurement and control processes.