How to check thermocouple with multimeter is a common question among technicians, electricians, and instrumentation engineers when a temperature measurement or gas appliance stops working properly. Before replacing a thermocouple, it is always advisable to test it using a digital multimeter. With basic electrical knowledge and a few simple checks, you can quickly determine whether the thermocouple is healthy or faulty.
This article explains what a thermocouple is, how it works, and three reliable methods to check a thermocouple using a multimeter.
What Is a Thermocouple?
A thermocouple is a temperature-sensing transducer that converts heat into a small electrical voltage. It works on the principle that when two dissimilar metals are joined together, a voltage is produced if there is a temperature difference between the junctions.
A typical thermocouple consists of:
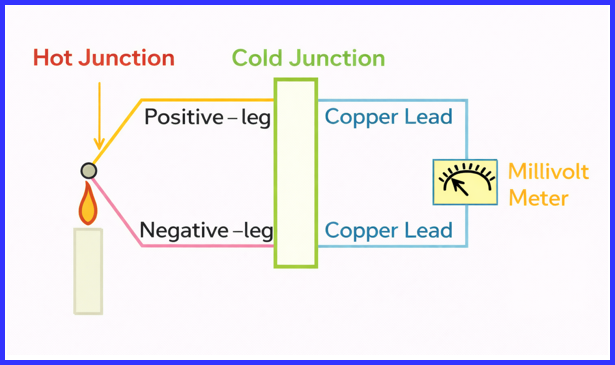
- Hot junction – placed at the point where temperature is measured
- Cold junction (reference junction) – kept at a known temperature
When the hot junction is heated, a voltage proportional to the temperature difference is generated. This voltage is then used for measurement, indication, or control in industrial and domestic applications.
Why Testing a Thermocouple Is Important
A faulty thermocouple can cause:
- Incorrect temperature readings
- Gas appliances to shut down
- Safety systems to malfunction
- Unnecessary replacement costs
Testing confirms whether the problem lies in the thermocouple or elsewhere in the system.
Tools Required to Check a Thermocouple With Multimeter
Depending on the test method, you may need:
- Digital multimeter (resistance & millivolt range)
- Crocodile clips or test leads
- Heat source (lighter or flame)
- Thermocouple adapter (for closed-circuit test)
Method 1: Resistance Test (Continuity Check)
Purpose
This test checks whether the thermocouple wire is electrically continuous.
Procedure
- Disconnect the thermocouple from the appliance.
- Set the multimeter to resistance (Ω) or continuity mode.
- Connect one probe to each end of the thermocouple.
- Observe the reading on the multimeter.
Expected Result
- A low resistance (a few ohms) indicates a good thermocouple.
- A high resistance (for example, 30–40 ohms or more) indicates a damaged thermocouple.
- In continuity mode, a continuous beep confirms a healthy thermocouple.
Method 2: Open Circuit Voltage Test
Purpose
This test checks whether the thermocouple generates sufficient voltage when heated.
Procedure
- Set the multimeter to the millivolt (mV) DC range.
- Connect the probes to both ends of the thermocouple.
- Heat the hot junction using a lighter or flame.
- Observe the voltage output.
Expected Result
- A healthy thermocouple used in gas appliances typically produces 25–30 mV.
- A reading close to 20 mV or lower indicates a weak thermocouple that should be replaced.
Method 3: Closed Circuit Test
Purpose
This is the most accurate test, as it checks the thermocouple under real operating conditions.
Procedure
- Install a thermocouple adapter into the gas valve.
- Screw the thermocouple into the adapter.
- Set the multimeter to millivolt range.
- Connect one probe to the adapter terminal and the other to the thermocouple body.
- Turn ON the appliance and allow it to operate normally.
Expected Result
- The voltage should be in the range of 12–15 mV.
- A reading below 12 mV indicates excessive voltage drop and a faulty thermocouple.
Common Reasons for Thermocouple Failure
- Aging and metal fatigue
- Oxidation at the hot junction
- Mechanical damage
- Improper flame contact
- Loose connections
Safety Tips While Testing Thermocouples
- Always disconnect power before resistance testing
- Use insulated probes and clips
- Avoid overheating the thermocouple
- Allow components to cool before handling
Applications Where Thermocouples Are Commonly Tested
- Gas stoves and ovens
- Boilers and heaters
- Furnaces
- Industrial temperature control systems
- Process plants
Conclusion
Knowing how to check thermocouple with multimeter helps in quick troubleshooting and avoids unnecessary replacements. By performing resistance, open-circuit, and closed-circuit tests, you can accurately assess the condition of a thermocouple. Regular testing ensures reliable temperature measurement, safe operation of gas appliances, and efficient industrial process control.
Read Next: