Gas flow measurement plays a critical role in industries such as oil & gas, power plants, refineries, petrochemicals, and process automation. Since gas volume changes with temperature and time, engineers frequently work with multiple flow units. This is why Gas Flow Formulas are essential for accurate calculations and conversions.
In this guide, you will learn the MMSCFD meaning, common gas flow units, and practical Gas Flow Formulas for conversions such as MMSCFD to SCFM, SCFM to MMSCFD, MMSCFD to Sm³/h, MMSCFD to Nm³/h, and more—explained step by step.
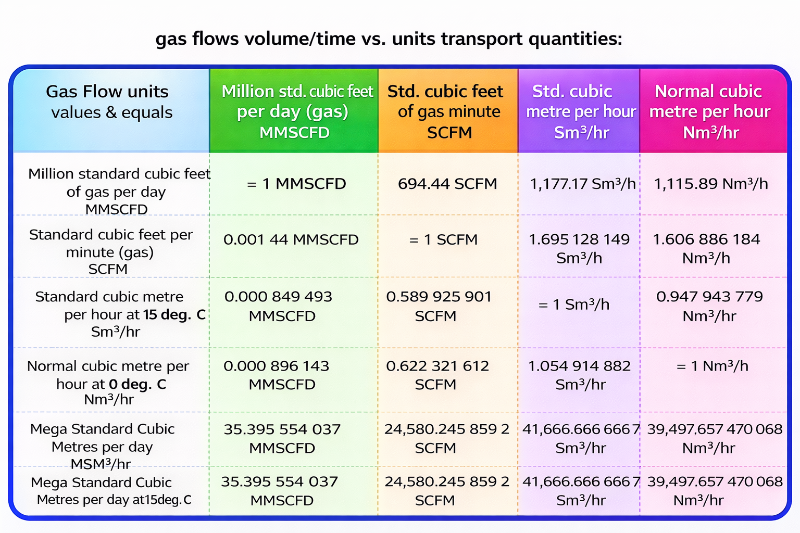
Gas Flow Units
Before applying gas flow formulas, it is important to understand the commonly used gas flow units.
1. SCFD (Standard Cubic Feet per Day)
SCFD represents the volume of gas flowing per day at standard pressure and temperature conditions.
2. SCFH (Standard Cubic Feet per Hour)
SCFH measures gas flow per hour under standard conditions.
3. SCFM (Standard Cubic Feet per Minute)
SCFM is widely used for compressors, blowers, and flow meters where instantaneous gas flow is required.
4. MMSCFD (Million Standard Cubic Feet per Day)
MMSCFD is used for large gas quantities in pipelines, gas wells, and processing plants.
MMSCFD Meaning
The MMSCFD meaning is straightforward:
1 MMSCFD = 1,000,000 Standard Cubic Feet of gas per day
This unit simplifies handling of very large gas volumes in industrial applications.
Gas Flow Rate Explained
Gas flow rate refers to the volume of gas passing through a system per unit time under defined reference conditions. Typically, standard conditions are:
- Pressure: 14.7 psi (1 atm)
- Temperature: 60°F (15.6°C)
Accurate gas flow rate calculations are essential for custody transfer, system design, equipment sizing, safety analysis, and energy accounting.
Constants for the Actual Gas Flow Calculation
The following constants are commonly used in Gas Flow Formulas:
- 1 MMSCFD = 1,000,000 SCFD
- 1 Day = 24 Hours
- 1 Hour = 60 Minutes
- 1 ft³ = 0.0283168 m³
- 1 m³ = 35.3147 ft³
Temperature Constants:
- 0°C in Kelvin: 273.15 K
- 15°C in Kelvin: 288.15 K
- 60°F in Kelvin: 288.81 K
Useful Ratios:
- 60°F / 15°C: 0.997714761
- 60°F / 0°C: 0.945777501
Note: Some values are rounded for practical engineering calculations.
Gas Flow Formulas and Conversions
MMSCFD to SCFD
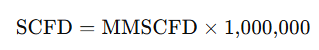
SCFD to MMSCFD
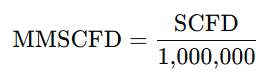
MMSCFD to SCFH
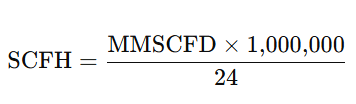
SCFH to MMSCFD
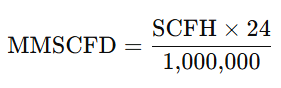
MMSCFD to SCFM Conversion
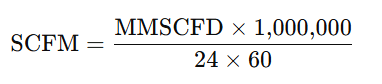
This MMSCFD to SCFM conversion is commonly used for flow meter calibration and compressor sizing.
SCFM to MMSCFD
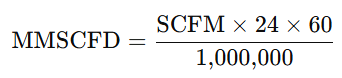
Gas Flow Rate by Volume and Temperature Conversion
MMSCFD to Sm³/h Conversion Formula
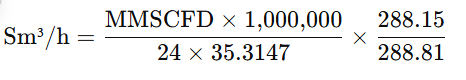
Where:
- 288.15 K = 15°C (standard condition)
- 288.81 K = 60°F
- 35.3147 = ft³ per m³
- 24 = hours per day
MMSCFD to Nm³/h Conversion Formula

Where:
- 273.15 K = 0°C (normal condition)
- 288.81 K = 60°F
Calculation Explanation
The letters S and N indicate gas reference conditions:
- Standard (S): 15°C
- Normal (N): 0°C
Both assume atmospheric pressure (1 atm or 101.325 kPa).
As temperature decreases, gas density increases. Therefore, the same mass of gas occupies less volume at normal conditions than at standard conditions.
Using the ideal gas law (PV = nRT), and keeping pressure and gas quantity constant:
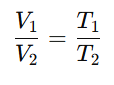
Practical Example
A gas well produces 140,000 SCFD at steady conditions.
Step 1: Convert to Sm³/day
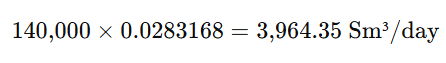
Step 2: Convert to Sm³/h
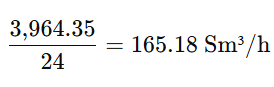
Step 3: Convert Sm³/h to Nm³/h
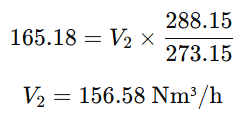
This confirms that Nm³/h is lower than Sm³/h due to the lower reference temperature.
Why Gas Flow Formulas Are Important
- Ensure accurate gas billing and custody transfer
- Support correct selection of flow meters and compressors
- Improve system efficiency and safety
- Prevent costly errors in large-scale gas calculations
Conclusion
Understanding Gas Flow Formulas is essential for anyone involved in gas flow measurement and instrumentation. Whether you are converting MMSCFD to SCFM, calculating Sm³/h or Nm³/h, or simply clarifying the MMSCFD meaning, the formulas explained here provide a reliable and practical reference for real-world applications.