Explore our comprehensive guide on the conversion of Kv to Cv and vice versa. With easy-to-follow formulas of Cv and Kv and practical examples, learn the differences between these flow coefficients for accurate fluid dynamics analysis.
In fluid mechanics, particularly when dealing with fluid flow through valves, pipes, and other components, the flow coefficients Cv and Kv play crucial roles. Engineers and technicians must understand these coefficients to design and maintain efficient fluid control systems. This article explores the relationship between Cv and Kv, including their definitions, the conversion between these units, and solved examples to illustrate their practical application.
Definitions
Cv
The flow coefficient, Cv, is primarily used in the United States. It defines the rate at which a valve will pass water (in US gallons per minute) at a temperature of 60°F, with a pressure drop across the valve of 1 psi.
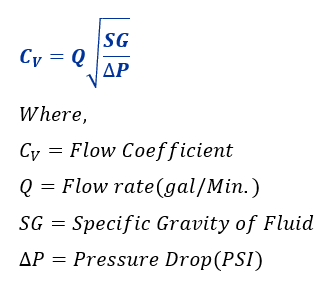
Kv
Conversely, Kv is commonly used in Europe and other parts of the world. It measures the water flow rate in cubic meters per hour (m³/hr) at a temperature of 5-30°C, with a pressure drop of 1 bar across the valve.

Relationship between Cv and Kv
The relationship between Cv and Kv is rooted in the conversion factors between the imperial units (used for Cv) and the metric units (used for Kv).
Cv to Kv Conversion

Thus, the below conversion formula can define the relationship between Cv and Kv.
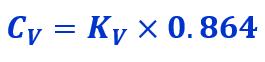
Kv to Cv Conversion
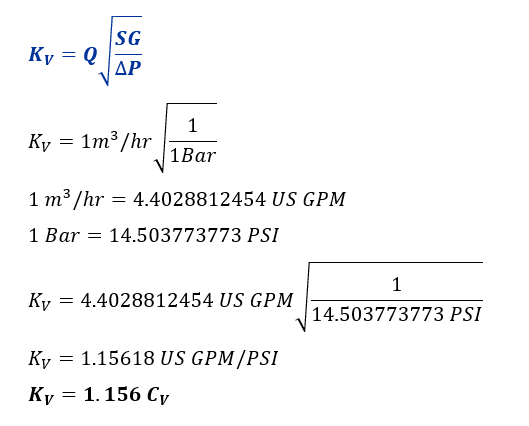
Thus, the below conversion formula can define the relationship between Kv and Cv.
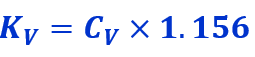
These conversions are crucial when working with international systems or when specifications are given in a different standard than one is accustomed to.
Solved Examples
Example 1: Converting Cv to Kv
Problem: A valve has a Cv of 10. Calculate its Kv.
Solution: Using the formula
𝐾v=𝐶v×0.864
=10×0.864
=8.64
Answer: The Kv of the valve is 8.64 m³/hr.
Example 2: Converting Kv to Cv
Problem: A valve has a Kv of 15. Calculate its Cv.
Solution: Using the formula
𝐶v=𝐾v×1.156
𝐶v=15×1.156
=17.34
Answer: The Cv of the valve is 17.34 US gallons per minute.
Example 3: Determining Flow Rate Using Cv
Problem: A valve with a Cv of 25 is used, and the pressure drop across the valve is maintained at 2 psi. Determine the flow rate of water through the valve.
Solution: The formula for flow rate Q (in US gallons per minute), given Cv and the pressure drop ΔP (in psi), is:
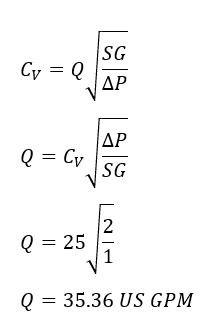
Answer: The flow rate through the valve is approximately 35.36 US gallons per minute.
Conclusion
Understanding the relationship between Cv and kV is essential for professionals working in fluid dynamics and related fields. It allows for accurate specification and analysis of valve performance across different measurement systems, ensuring compatibility and efficiency in global projects. Whether you are designing a new system, troubleshooting, or merely trying to understand the specifications of a given valve, the ability to convert between Cv and Kv and apply these concepts practically can significantly enhance your effectiveness.
Read Next: