A keyphasor is a critical reference signal used in rotating machinery monitoring systems. In vibration analysis and condition monitoring, the keyphasor provides precise information about shaft position, speed, and phase angle.
Without a keyphasor signal, it is almost impossible to accurately analyze rotor behavior, identify imbalance, or perform phase-based vibration diagnostics. For machines like turbines, compressors, motors, and generators, the keyphasor acts as the timing reference for all dynamic measurements.
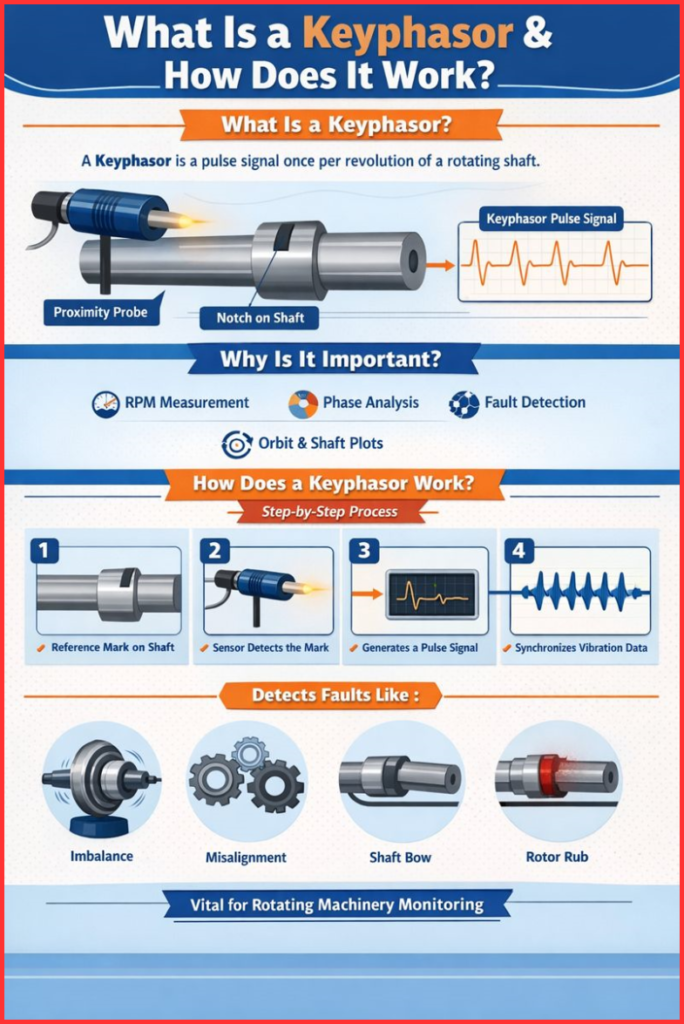
What Is a Keyphasor?
A keyphasor is a once-per-revolution (1× RPM) reference pulse generated from a rotating shaft. It is typically obtained using a proximity probe, optical sensor, or magnetic pickup that detects a physical reference on the shaft, such as:
- A keyway
- A notch
- A drilled hole
- A reflective tape or mark
Each time this reference point passes the sensor, the keyphasor produces a pulse. This pulse represents a fixed angular position of the shaft and is used as a reference for vibration and phase measurements.
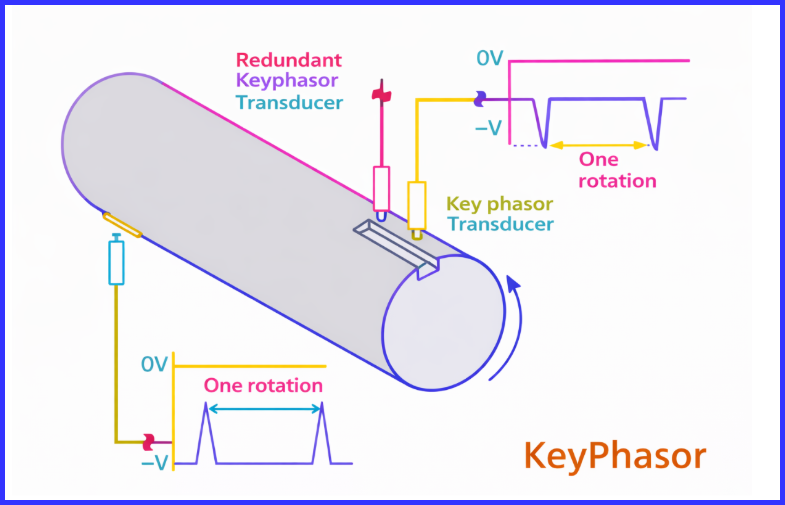
In simple terms, the keyphasor tells the monitoring system “this is the exact position of the shaft right now.”
Keyphasor is a registered trademark of Bently Nevada. A typical Keyphasor system consists of three main components: a proximity probe, an extension cable, and a Proximitor® sensor. According to industry conventions, the primary Keyphasor reference point is normally installed on the driving end of the machine, ensuring accurate and consistent shaft phase measurement.
Why Is a Keyphasor Important?
The keyphasor signal is essential for advanced vibration diagnostics. Its main purposes include:
- Measuring shaft rotational speed (RPM)
- Providing phase reference for vibration signals
- Enabling orbit plots and shaft centerline plots
- Supporting order analysis and synchronous vibration analysis
- Identifying faults such as imbalance, misalignment, bent shafts, and rubs
Without a keyphasor, vibration data is limited to overall amplitudes and frequencies, reducing diagnostic accuracy.
Role of Keyphasor Signal in Vibration Monitoring and Rotor Balancing
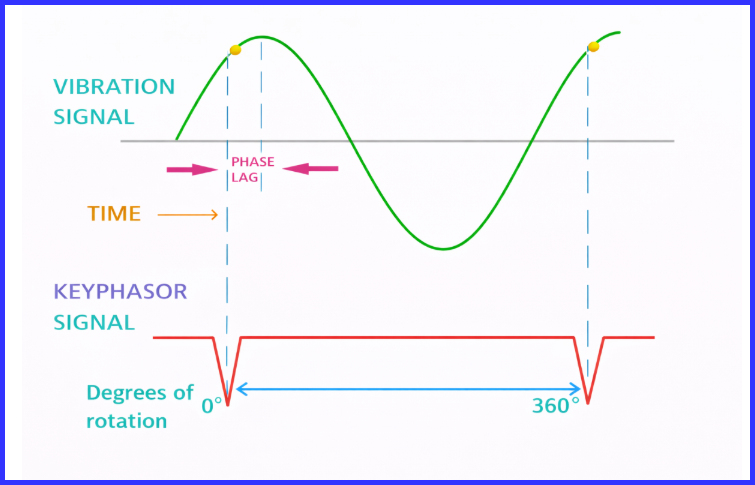
The Keyphasor signal is widely used in machine monitoring, diagnostics, and asset management systems to produce filtered vibration data. It helps extract critical information such as vibration amplitude, phase angle, shaft speed, and several other important parameters. Among these, phase information is especially vital. Without accurate phase data, assessing overall machine health and identifying specific faults becomes extremely challenging.
A Keyphasor provides a precise angular reference for the rotating shaft, typically defining one complete revolution from 0 to 360 degrees. During vibration analysis, close attention is given to the 1X and 2X vibration components, where X represents the machine’s running speed. While vibration sensors measure signals across a wide frequency range, the Keyphasor allows the system to accurately determine the actual shaft speed.
For example, if a machine operates at 5,000 RPM, the Keyphasor enables the analyzer to isolate vibration at 5,000 RPM (83.33 Hz). This filtered signal makes it possible to observe shaft motion and orbital behavior within the bearing. The phase angle is calculated as the time difference between the Keyphasor pulse and the first positive peak of the vibration waveform.
In turbomachinery, the Keyphasor plays a crucial role in determining the phase angle of unbalance mass during dynamic balancing. Proper balancing of turbine rotors is essential for reliable and safe operation. Although manufacturers may balance rotors in the factory using alternative reference methods, field balancing at the user’s site requires a Keyphasor signal. Without it, accurate turbine rotor balancing is not feasible.
How Does a Keyphasor Work?
The working principle of a keyphasor is based on detecting a known reference point on a rotating shaft and converting it into an electrical pulse.
Step-by-Step Working of a Keyphasor
- Reference Mark on Shaft
A physical feature such as a keyway or notch is provided on the shaft. This serves as the angular reference. - Sensor Detection
A proximity probe (commonly eddy current type) is installed near the shaft. As the reference mark passes under the probe, the sensor detects a change in distance or material. - Pulse Generation
The sensor generates a sharp electrical pulse once per revolution. This pulse is the keyphasor signal. - Signal Processing
The keyphasor pulse is sent to a vibration monitoring system or analyzer, where it is used as a timing reference. - Synchronized Analysis
Vibration signals from accelerometers or proximity probes are synchronized with the keyphasor, enabling phase and order-based analysis.
Types of Keyphasor Sensors
Depending on the application, different sensors can be used to generate a keyphasor signal:
- Eddy Current Proximity Probe (most common in turbomachinery)
- Optical Sensor (uses reflective tape or mark)
- Magnetic Pickup (used in gear or toothed wheel applications)
- Hall Effect Sensor (used in low-speed machines)
Keyphasor Signal Characteristics
A proper keyphasor signal should have:
- One clean pulse per shaft revolution
- Stable amplitude
- Minimal noise or false triggering
- Correct phase alignment with vibration probes
Poor keyphasor quality can lead to incorrect diagnostics and misleading vibration plots.
Applications of a Keyphasor
Keyphasors are widely used in:
- Steam and gas turbines
- Centrifugal compressors
- Large electric motors and generators
- Pumps and fans
- Condition monitoring and protection systems
They are especially critical in high-speed and critical rotating machinery.
Common Faults Detected Using a Keyphasor
With a reliable keyphasor signal, engineers can detect:
- Rotor imbalance
- Angular and parallel misalignment
- Shaft bow or eccentricity
- Mechanical looseness
- Rotor rubs and instability
Conclusion
The keyphasor is a vital component in modern rotating machinery monitoring systems. By providing a precise once-per-revolution reference, the keyphasor enables accurate speed measurement, phase analysis, and advanced vibration diagnostics.
Understanding how a keyphasor works and how it integrates with vibration sensors helps maintenance and reliability engineers detect faults early, reduce downtime, and ensure safe machine operation. In short, without a keyphasor, true condition-based monitoring of rotating equipment is incomplete.
Read Next: