In flow measurement systems, accuracy does not depend only on the transmitter or piping arrangement. One small dimension plays a very big role—the orifice beta ratio. Incorrect selection of this ratio can lead to poor accuracy, excessive pressure loss, and even damage to the process equipment.
In this article, you will clearly understand what is beta ratio, how the orifice plate beta ratio affects flow measurement, and why engineers usually keep this ratio within a safe and reliable range.
What Is Orifice Beta Ratio?
The orifice beta ratio (β) is defined as the ratio of the orifice bore diameter to the internal diameter of the pipe.
Mathematical Expression of Beta Ratio

β=Pipe Internal Diameter (D)Orifice Bore Diameter (d)
This simple ratio controls how much restriction is created in the flow path and directly influences the pressure drop across the orifice plate.
What Is Beta Ratio in an Orifice Plate?
When we talk about what is beta ratio, we are essentially describing how large the orifice opening is compared to the pipe size.
- A large beta ratio means a bigger opening and less restriction
- A small beta ratio means a smaller opening and more restriction
This balance is extremely important in differential pressure–based flow measurement.
Extreme Cases of Orifice Beta Ratio
To understand the significance of the beta ratio, let us look at some extreme conditions.
Case 1: Beta = 1
If the orifice bore diameter equals the pipe internal diameter:
- No flow restriction exists
- Pressure drop becomes zero
- Differential pressure cannot be measured
Result: Flow measurement is not possible.
Case 2: Very High Beta (β > 0.7)
When the orifice plate beta is close to 1:
- Very small pressure drop is generated
- Signal becomes weak and unstable
- Measurement uncertainty increases
That is why standards recommend not exceeding a beta ratio of 0.7.
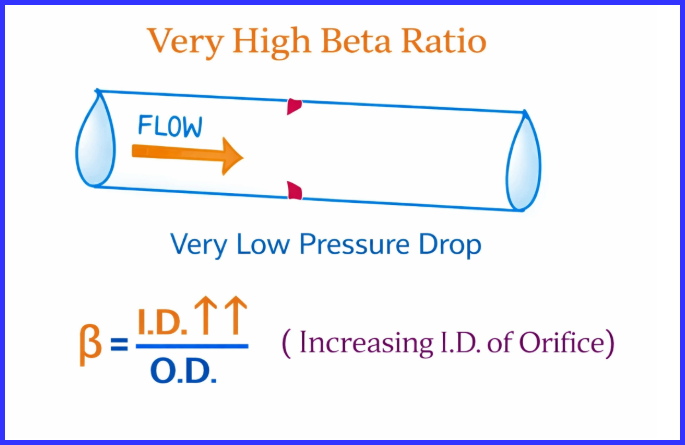
Case 3: Very Low Beta Ratio (β < 0.3)
If the beta ratio orifice plate is very small:
- Flow restriction becomes very high
- Excessive pressure loss occurs
- Pump energy requirement increases
Although pressure drop is easy to measure, this condition creates serious process problems.
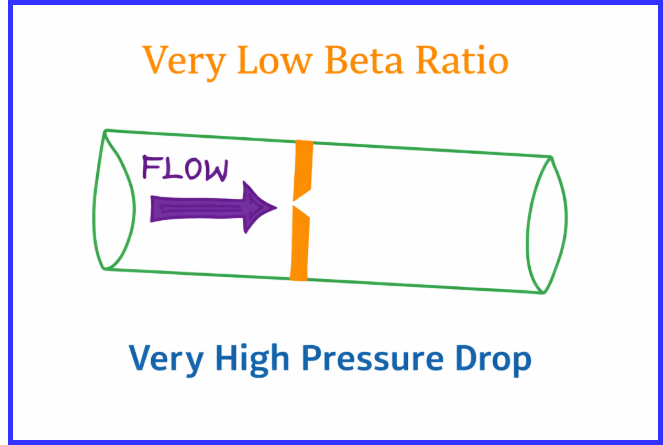
Why Orifice Beta Ratio Is Kept Between 0.3 and 0.7
The recommended beta ratio range of 0.3 to 0.7 is not arbitrary. It is based on decades of experimental data and field experience.
Let us understand the reasons one by one.
1. Pressure Drop and Process Efficiency
A very low beta ratio causes unnecessary pressure loss. This forces pumps or compressors to work harder, leading to:
- Higher power consumption
- Increased operating cost
- Reduced overall system efficiency
Process engineers usually specify a maximum allowable pressure loss, which limits how low the beta ratio can be.
2. Risk of Cavitation and Flashing
As pressure drops across the orifice:
- Liquid may reach its vapor pressure
- Vapor bubbles may form and collapse
This phenomenon leads to cavitation and flashing, which can:
- Damage pipelines and instruments
- Create noise and vibration
- Reduce measurement reliability
Lower beta ratio values significantly increase this risk.
3. Effect on Coefficient of Discharge (Cd)
The coefficient of discharge (Cd) is not constant. It depends on:
- Reynolds number
- Beta ratio
According to API and ISO standards:
- At high Reynolds numbers, uncertainty mainly depends on beta ratio
- Extremely high or low beta ratios increase measurement uncertainty
A moderate beta ratio (around 0.5) provides better accuracy and repeatability.
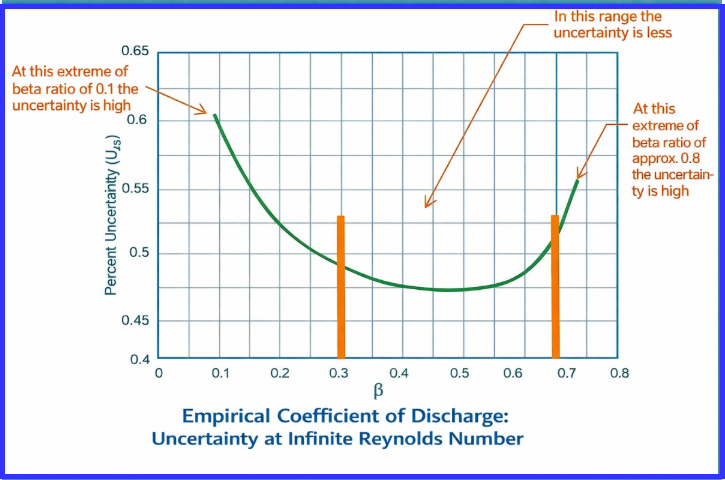
4. Measurement Uncertainty and Accuracy
Experimental data shows that:
- Uncertainty increases sharply at extreme beta ratios
- Mid-range beta values offer stable flow profiles
That is why most designers prefer a beta ratio orifice plate close to 0.5 whenever possible.
Typical Recommended Orifice Beta Ratio Range
| Standard Practice | Recommended Beta Ratio |
| Common Industry Use | 0.3 – 0.7 |
| Some Standards | 0.2 – 0.6 |
| Best Accuracy Zone | Around 0.5 |
There is no hard rule, but these limits are established through empirical testing and long-term operational experience.
Key Takeaways on Beta Ratio
- The beta ratio defines flow restriction and pressure drop
- Too high beta → low pressure signal and high uncertainty
- Too low beta → excessive pressure loss and cavitation risk
- A moderate beta ratio ensures accuracy, safety, and efficiency
Conclusion
The orifice beta ratio is one of the most critical parameters in orifice plate flow measurement. Keeping the beta ratio within a reasonable range ensures reliable readings, protects process equipment, and minimizes energy losses.
While there is flexibility in selection, practical experience and international standards clearly show that staying between 0.3 and 0.7, with an ideal value near 0.5, offers the best balance between accuracy and process performance.
Selecting the right beta ratio orifice plate is not just a calculation—it is good engineering practice.
Read Next: