Override control is a control strategy used in industrial processes to ensure a system’s safety and operational efficiency by automatically selecting the most critical variable to control among several competing ones. This method comes into play when multiple process variables must be controlled, but only one can be prioritized at any time due to safety or process constraints. Override control ensures the system operates within safe and optimal conditions, even in disturbances or abnormal conditions.
What is Override Control?
Override control uses multiple controllers, each responsible for a specific process variable. However, instead of having these controllers operate independently, an override controller (or selector) determines which variable is most critical at any given moment and overrides the others to take control of the final control element (e.g., a valve or actuator). This ensures that the most critical variable is maintained within its desired range, thus preventing unsafe conditions or equipment damage.
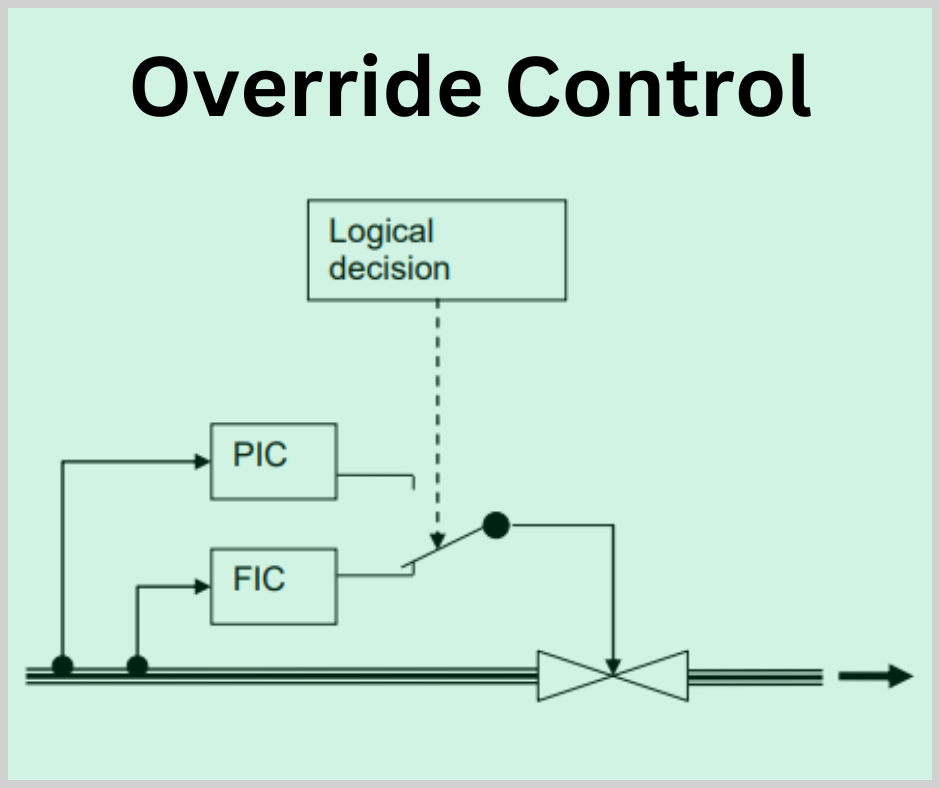
Need for Override Control
- Safety Concerns: In many industrial processes, maintaining certain variables within specific limits is crucial for safety. For example, in a chemical reactor, both temperature and pressure need to be controlled to prevent hazardous conditions. Override control can prioritize these variables based on their criticality to safety.
- Operational Efficiency: Override control helps optimize process performance by ensuring that the most critical process variable is always under control. This leads to more efficient operation and better resource utilization.
- Disturbance Management: Industrial processes are often subject to disturbances affecting multiple variables. Override control allows the system to dynamically adjust which variable is controlled, providing a robust response to disturbances and maintaining stable operation.
- Equipment Protection: By prioritizing control of critical variables, override control can protect equipment from damage. For instance, in a boiler system, controlling pressure to prevent overpressure conditions can protect the boiler from damage.
Applications of Override Control
- Chemical Processing: In chemical reactors, override control is used to maintain critical variables like temperature and pressure. If the temperature starts to rise to unsafe levels, the override controller can prioritize temperature control over other variables to prevent a runaway reaction.
- Oil and Gas Industry: In drilling operations, maintaining control of parameters such as drill pressure and flow rates is crucial. Override control ensures that the most critical parameter, which could impact safety or efficiency, is always controlled.
- Power Plants: In boiler control systems, override control is used to manage steam pressure and water levels. By prioritizing the most critical variable, the system ensures safe and efficient operation of the boiler.
- HVAC Systems: In heating, ventilation, and air conditioning systems, override control can be used to prioritize temperature control in critical zones, ensuring comfort and safety in those areas.
- Manufacturing: In processes such as metal forming or plastic extrusion, override control can manage critical parameters like pressure and temperature to ensure product quality and equipment protection.
- Water Treatment Plants: In water treatment facilities, override control can be used to maintain critical parameters like pH and chlorine levels, ensuring water quality and safety.
Benefits of Override Control
- Enhanced Safety: By ensuring that the most critical variables are always controlled, override control significantly enhances the safety of the process and prevents hazardous conditions.
- Improved Efficiency: Override control helps in optimizing the overall process efficiency by dynamically prioritizing the control of variables based on real-time conditions.
- Robust Performance: The system can handle disturbances more effectively by switching control to the most critical variable, thus maintaining stable and reliable operation.
- Equipment Protection: Override control prevents damage to equipment by ensuring that critical variables are controlled within safe limits, thereby extending the lifespan of the equipment.
In conclusion, override control is an essential strategy in many industrial processes, providing a way to prioritize and manage critical variables dynamically. This approach ensures safety, improves operational efficiency, and protects equipment, making it invaluable in complex and potentially hazardous environments.
Read Next: